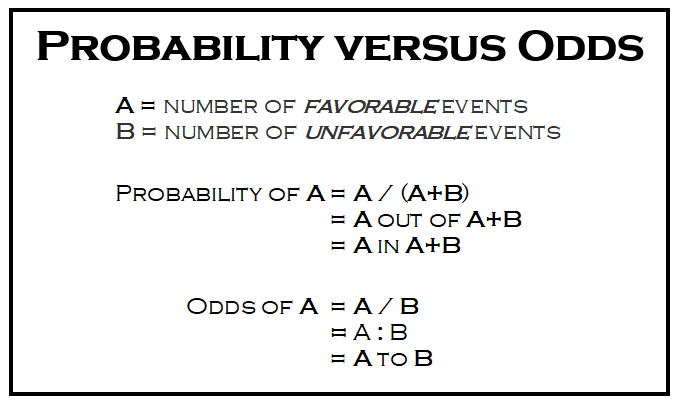
Odds is a see also of probability As nouns the difference between odds and probability is that odds is the ratio of the probabilities of an event happening to that of it not happening while probability is the state of being probable; The product of that division is called the odds ratio (OR) In our example, the odds of delivering a premature baby in smokers is 8 / 42, which comes out to 019 The odds of delivering a premature baby in nonsmokers is 13 / 87, which comes out to 015 The OR is 019 / 015, or about 127An odds ratio (OR) is a statistic that quantifies the strength of the association between two events, A and B The odds ratio is defined as the ratio of the odds of A in the presence of B and the odds of A in the absence of B, or equivalently (due to symmetry), the ratio of the odds of B in the presence of A and the odds of B in the absence of ATwo events are independent if and only if

Ppt Conditional Probability Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id
Is a higher odds ratio better
Is a higher odds ratio better- ods ratio = posterior odds prior odds = 016 0061 = 262 This tells us that the odds of having cancer are increased by 262 times given the positive test result An odds ratio is example of what we will later call an effect size, which is a way of quantifying how relatively large any particular statistical effect isThe odds of winning are 1/9,999 () and the probability of winning is 1/10,000 () In this case, odds and probability are essentially identical Relative Risk (RR) & Odds Ratio (OR) The difference between odds and probability is important because Relative Risk is calculated with probability and Odds Ratio is calculated with odds



1
• Probability is expressed as a number between 0 and 1, while Odds is expressed as a ratio • Probability ensures that an event will occur, but Odds is used to find out whether the event will ever occur Say for example the odds are represented as 25, this would imply that for every 1 you wager, you will gain a profit of 15 if the outcome was in your favor Here, to convert odds ratio to probability in sports handicapping, we would have the following equation (1 / the decimal odds) * 100 or (1 / 25) * 100Many people wrongfully assume odds and probabilities are the same thingThey're definitely not, as there's a significant difference between saying there are
Odds (Safety) = 12/72 = 1787 Now get out your calculator, because you'll see how these relate to each other Odds (Accident) = Pr (Accident)/Pr (Safety) = 053/947 Understanding Probability, Odds, and Odds Ratios in Logistic Regression Despite the way the terms are used in common English, odds and probability are not interchangeable Binomial So I think that the reason you see lots of RR, but very little PR is that PR is constructed from probability/Binomial type quantities, while RR is constructed from rate type quantities In particular note that incidence can exceed 100% if people can catch the disease multiple times per year, but probability can never exceed 100%Ratio Pot Odds / Ratio It is not just number from percentage but it is upside down pot size amount you have to call pot was $80 and they bet $ $100 pot and call $ = 5 1 You are risking $1 to win $5 Now the pot is $1 Hand Odds (cards left outs)/outs If you have 8 outs on the turn then (468)/8 = 475 1 or (1 fraction
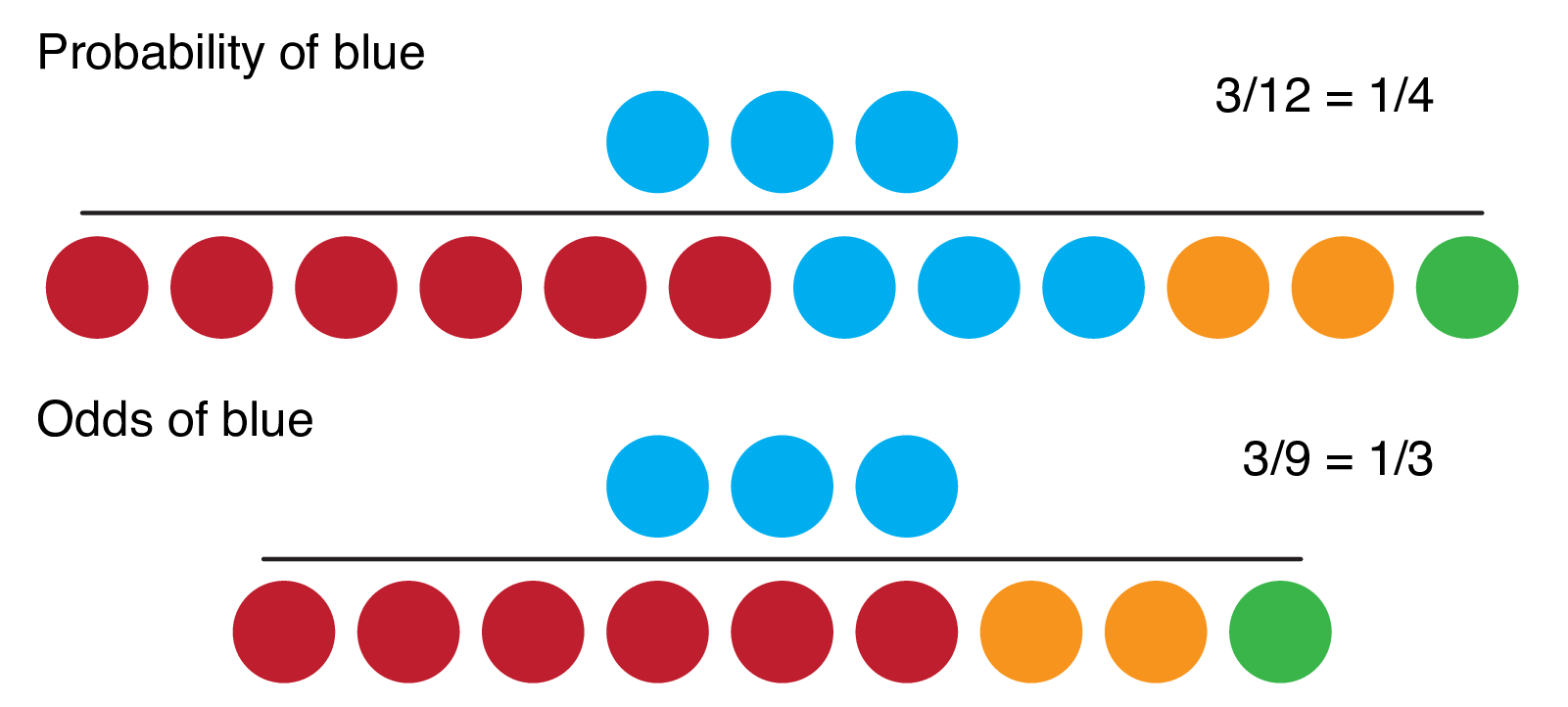
Odds, on the other hand, are the ratio of favorable outcomes to unfavorable outcomes The denominator contains ONLY the marbles that aren't the favorable outcomes Odds uses the contexts of good outcomes and bad outcomes Written as fractions, these two values are completely different Probability is 1/4 while odds in favor are 1/3 That is a ratio of 100 to 500, or simply 1 to 5 To express the (statistical) Odds against, the order of the pair is reversed Hence the Odds against rolling a A highly simplified example illustrates this Suppose that 18 out of patients (90 percent probability, odds of 91) in an experiment lost weight while using diet A, while 16 out of (80 percent, odds of 41) lost weight using diet B The relative risk of losing weight by choosing diet A over diet B is 1125, while the odds ratio is about 225




Odds Ratio Sage Research Methods




Odds Ratios And Risk Ratios Youtube
1 Log Odds Ratio Log odds ratio is a statistical tool to find out the probability of happening one event out of 2 events In our case, its finding out which words are more or less likely to come from each book Here n is number of times that word is used by each scientist and total is total words by each one of themHow to calculate the probability, odds for, and odds against an event occurringAs the name implies, the odds ratio is a ratio of two odds Just as relative risk assesses how one probability measures up to another, the odds ratio assesses how one odds measures up to another



Ctspedia Ctspedia Oddsterm
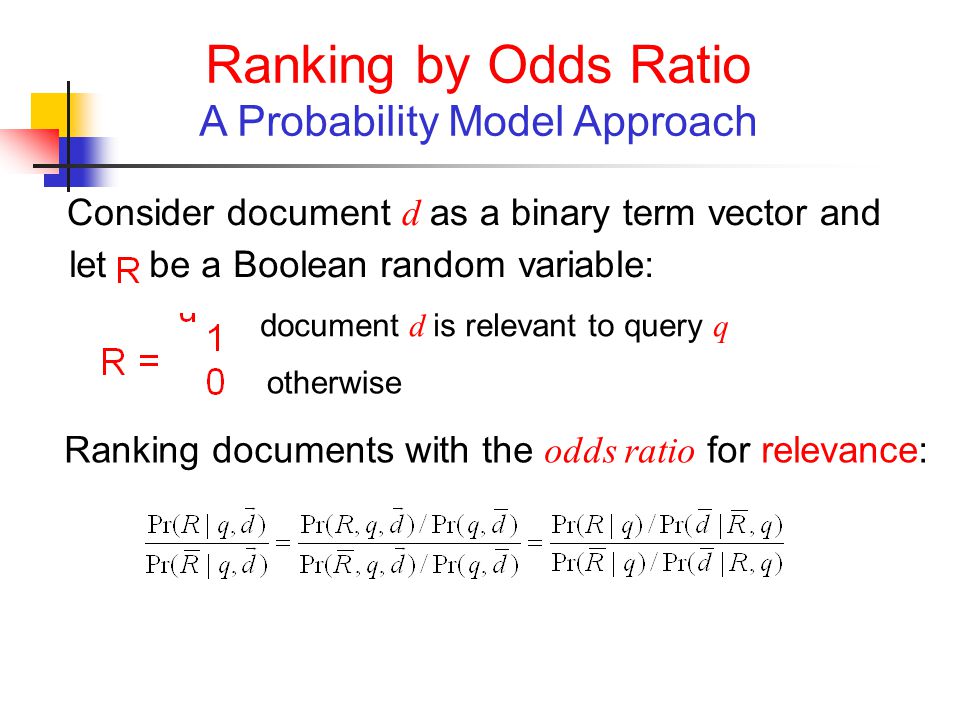



Ranking By Odds Ratio A Probability Model Approach Let Be A Boolean Random Variable Document D Is Relevant To Query Q Otherwise Consider Document D As Ppt Download
8 e b = e log(odds male /odds female) = odds male /odds female = OR which means the the exponentiated value of the coefficient b results in the odds ratio for gender In our particular example, e = 544 which implies that the odds of being admitted for males is Converting Odds to Probability Simply add the 2 components of the odds together to make a new denominator, and use the old numerator eg If the odds are 35, or 3 to 5, the probability is 3 ÷ (35) = 3/8 = 375% Converting Probability to Odds Take the probability, and divide it by its compliment = (1itself) eg OR (a/c)/ (b/d) = ad∗cb The risk, or probability, and the odds are related with the following formula risk = Odds 1 odds from which we can infer that if the risk or the probability of failure is low ( P




How To Calculate Odds Ratios And Probabilities In Case Control Studies Cross Validated



Odds Vs Probability Vs Chance Data Science Central
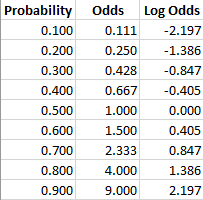
This is equivalent to the same statement that if the prior odds for spam are $16$ and the likelihood ratio for the spam filter being triggered is $41$ then the posterior odds for spam given the spam filter is triggered is $46$ The probability that an event will occur is the fraction of times you expect to see that event in many trials Probabilities always range between 0 and 1 The odds are defined as the probability that the event will occur divided by the probability that the event will not occur If the probability of an event occurring is Y, then the probability of the event not occurring is 1Y When the probability is small (




A Most Odd Ratio American Journal Of Preventive Medicine



1
The smaller the probability, the more similar probability and odds will be For example, the probability of winning the UK National Lottery is The odds are The larger the probability, the larger the difference with the odds High probabilities have astronomical odds A probability of 90% equates to oddsIn statistics, odds are an expression of relative probabilities, generally quoted as the odds in favorThe odds (in favor) of an event or a proposition is the ratio of the probability that the event will happen to the probability that the event will not happen Mathematically, this is a Bernoulli trial, as it has exactly two outcomesIn case of a finite sample space of equally likely outcomesOdds ( female) = 7 / 3 = odds ( male) = 3 / 7 = We could use this information to compute an odds ratio O R = / = 544 Thus a female is 544 times more likely to get in But since the probability of an event is just p p q the probability of a male getting in is 30%, while the probability of a female getting




Epi546 Block I Lecture 3 Frequency How Do




Statistical Analysis Sc504 Hs927 Spring Term Ppt Video Online Download
Fractional odds are sometimes called British odds or traditional odds and are sometimes written as a fraction, such as 6/1, or expressed as a ratio, like sixtoone Decimal odds represents the Odds can be expressed as a ratio of the probability an event will happen divided by the probability an event won't happen Odds in favor of A = A / (1 A), usually simplified to lowest terms, For instance, if the probability of an event occurring is 075, then the odds for it happening are 075/025 = 3/1 = 3 to 1 for, while the probability that it doesn't occur is 1 to 3 against Risk vs odds The terms 'risk' and 'odds' are often used interchangeably but they actually have quite different implications and are calculated in different ways Odds is a concept that is very familiar to gamblers It is a ratio of probability that a particular event will occur and can be any number between zero and infinity




Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios




What And Why Of Log Odds What Are Log Odds And Why Are They By Piyush Agarwal Towards Data Science
A fractional listing of 6/1 (sixtoone) odds would mean that you win $6 against every $1 you wager, in addition to receiving your dollar back (ie, the amount you wagered) I'm trying to figure out the true odds of a given horse winning a race against other horses Before a race, odds are posted on a big board horse A is 21, horse B is 51, etc Let's assume these odds are accuratethat is, the betting is spoton The problem is that when you sum these odds they come out to more than 100% Here's a recent race It's a ratio of events to nonevents You can switch back and forth between probability and odds—both give you the same information, just on different scales If O1 is the odds of event in the Treatment group and O2 is the odds of event in the control group then the odds ratio is O1/O2




Relative Risk Odds Ratios Youtube
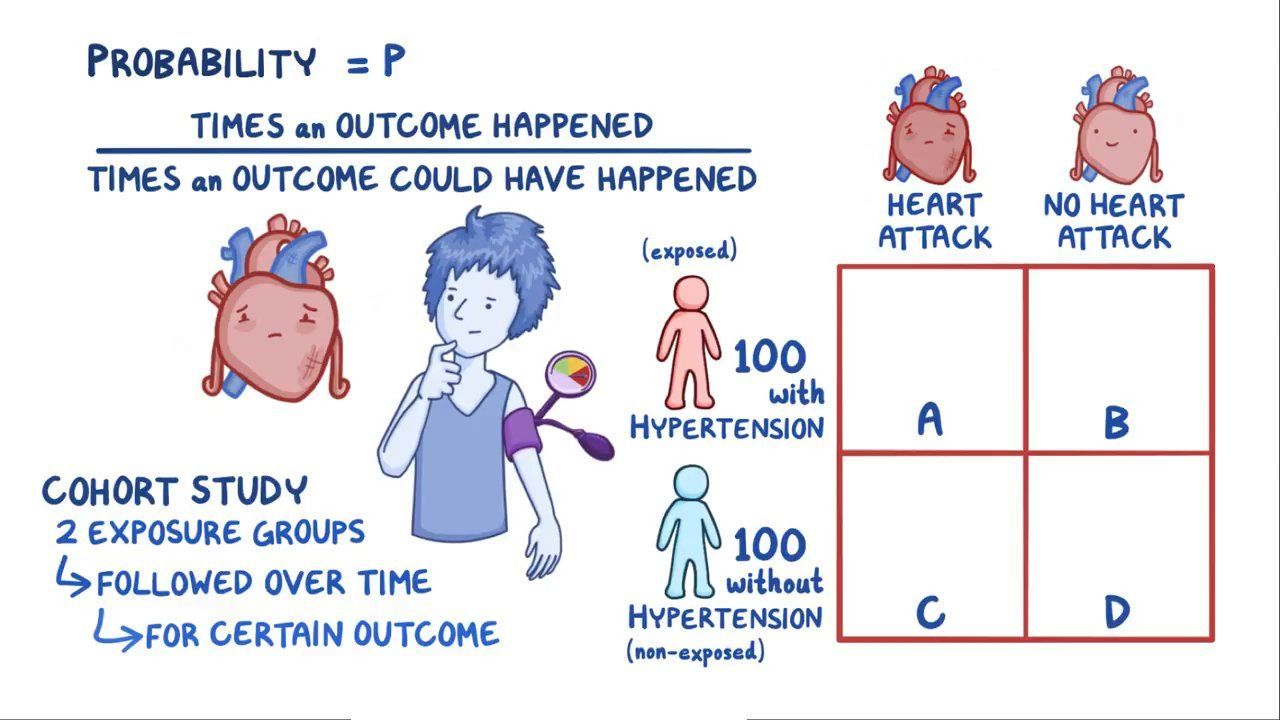



Odds Ratio Osmosis
Pretest odds × Likelihood ratio = Posttest odds To use this formulation, probabilities must be converted to odds, where the odds of having a disease are expressed as the chance of having the disease divided by the chance of not having the disease For instance, a probability of 075 is the same as 31 odds (Figure 1–8)The magnitude of the odds ratio is called the "strength of the association" The further away an odds ratio is from 10, the more likely it is that the relationship between the exposure and the disease is causal For example, an odds ratio of 12 is above 10, but is not a strong association An odds ratio of 10 suggests a stronger associationThe odds ratio is a common measure of risk but its interpretation may be hazardous The risk ratio is a ratio of probabilities, which are themselves ratios The numerator of a probability is the number of cases with the outcome, and the denominator is the total number of cases




Ppt Conditional Probability Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id
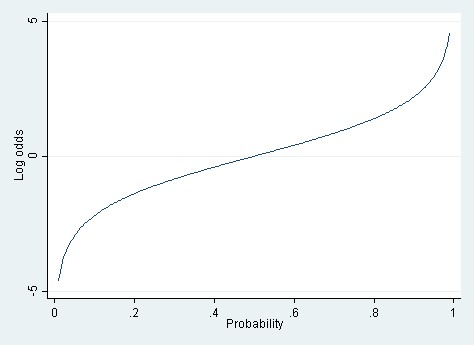



Linear Vs Logistic Probability Models Which Is Better And When Statistical Horizons
The odds ratio comparing the new treatment to the old treatment is then simply the correspond ratio of odds (01/09) / (02/08) = 0111 / 025 = 0444 (recurring) This means that the odds of a bad outcome if a patient takes the new treatment are 0444 that of the odds of a bad outcome if they take the existing treatmentFrom probability to odds to log of odds Everything starts with the concept of probability Let's say that the probability of success of some event is 8 Then the probability of failure is 1 – 8 = 2 The odds of success are defined as the ratio of the probability of success over the probability The odds ratio is the ratio of two odds ODDS RATIO Odds Ratio = Odds of Event A / Odds of Event B For example, we could calculate the odds ratio between picking a red ball and a green ball The probability of picking a red ball is 4/5 = 08 The odds of picking a red ball are (08) / 1(08) = 08 / 02 = 4 The odds ratio for picking a red




Probability Odds Odds Ratio Youtube
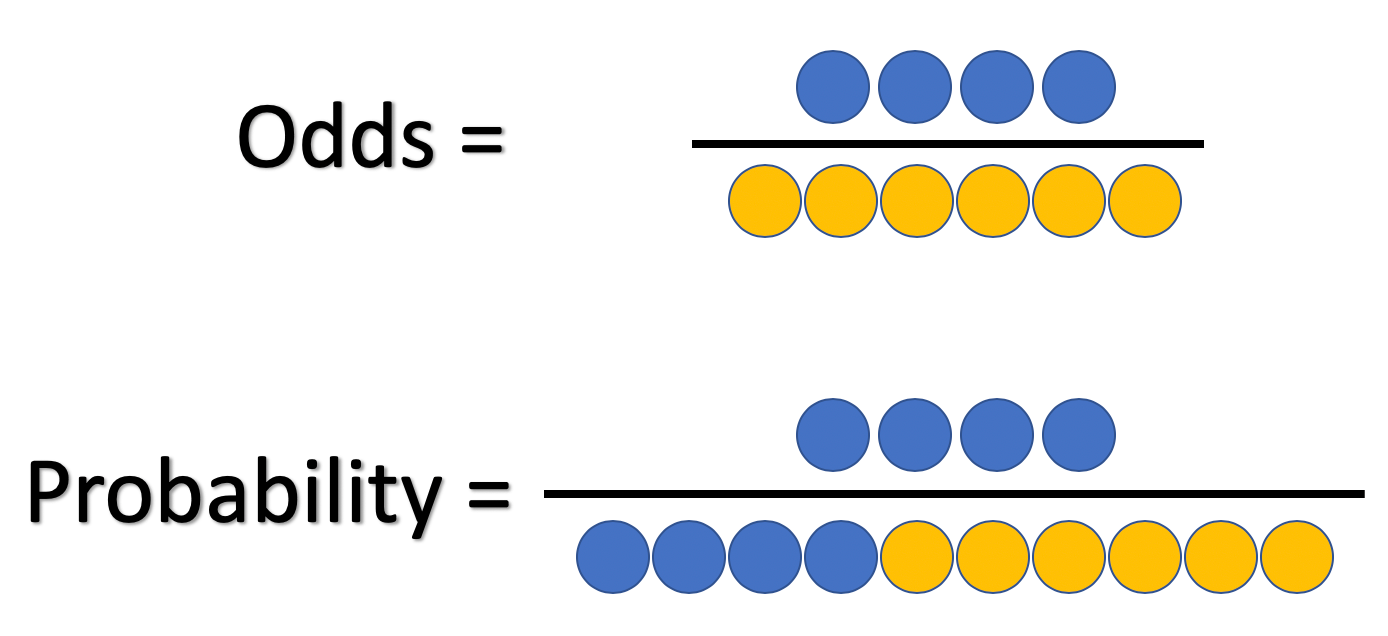



What And Why Of Log Odds What Are Log Odds And Why Are They By Piyush Agarwal Towards Data Science
Odds Ratio (OR) measures the association between an outcome and a treatment/exposure Or in other words, a comparison of an outcome given two different groups (exposure vs absence of exposure) OR is a comparison of two odds the odds of an outcome occurring given a treatment compared to the odds of the outcome occurring without the treatment Probability is a branch of mathematics, which includes odds One can measure chance, with the help of odds or probability While odds are a ratio of occurrence to nonoccurrence, the probability is the ratio of occurrence to the wholeA comparison of odds, the odds ratio, might then make sense OR= ˇ 1 1 ˇ 1 ˇ 2 1 ˇ 2 Odds ratio for the Titanic example is OR= 376 037 = 1016 This is very different from the relative risk calculated on the same data and may come as a surprise to some readers who are accustomed of thinking of odds ratio as of relative risk (Greenland, 1987)



Introduction To Genetic Epidemiology Lesson 5 Analyzing The Data
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dotdash_Final_The_Math_Behind_Betting_Odds_and_Gambling_Nov_2020-01-735accb453c8424b9e063c2c14e4edf4.jpg)



The Math Behind Betting Odds Gambling
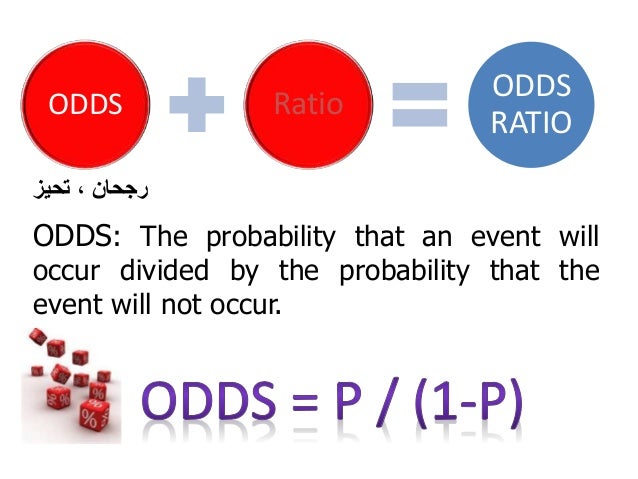
Englishwise, they are correct it is the odds and the odds are based on a ratio calculation It is not , however, the odds ratio that is talked about when results are reported The odds ratio when results are reported refers to the ratio of two odds or, if you prefer, the ratio of two odds ratios That is, let us write Probability (of success) is the chance of an event happening For example, there might be an 80% chance of rain today Odds are the probability of success (80% chance of rain) divided by the probability of failure (% chance of norain) = 08/02 = 4, or 4 to 1 Logodds is simply the logarithm of odds 1Odds and Odds Ratios Odds are the probability of an event happening / the probability of an event not happening Thus the odds of throwing a three with one die is 1/5 odds = probability / (1 probability)




Summary Of Odds Ratios Logarithmic Scale And Probability Of X 2 For Download Table




Odds Ratios Versus Relative Risk
In odds ratio, we take ratio of those odds in two different groups Step 1 At first, we calculate the odds in those comparison groups Cases Odds that a case was exposed = Probability of exposures in cases / Probability of nonexposures in cases = Number of exposed among cases (a) / total number of cases (ac) / Number of not exposed among Odds Odds seems less intuitive It is the ratio of the probability a thing will happen over the probability it won't In the spades example, the probability of drawing a spade is 025 The probability of not drawing a spade is 1 025 So the odds is 025/075 or 13 (or 033 or 1/3 pronounced 1 to 3 odds) Moving back and forth The odds are defined as the probability that the event will occur divided by the probability that the event will not occur A probability of 0 is the same as odds of 0 Probabilities between 0 and 05 equal odds less than 10 A probability of 05 is the same as odds of 10 Think of it this way The probability of flipping a coin to heads is 50%



Ctspedia Ctspedia Oddsrisk




Evaluating Results The Best Evidence So Far Weve
1 Probability = Event/Sample Space 2 Odds= Prob (Event)/Prob (NonEvent) 3 Odds Ratio = Odds (Group 1)/ Odds (Group 2) Interpretation The Odds Ratio is a measure of association between exposure and outcome OR=Odds (Group 1)/Odds (Group2)>1 indicates the increased occurrence of an event in Group 1 compared to Group 2
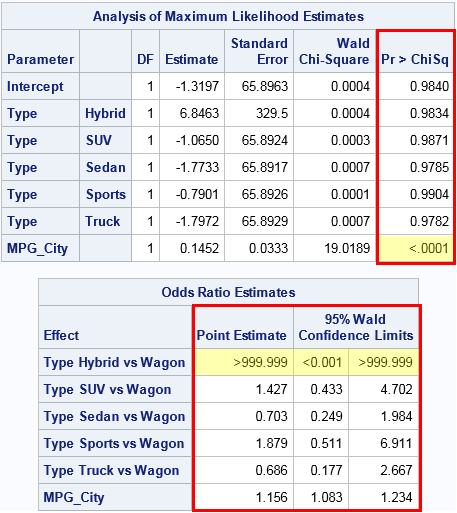



Formats For P Values And Odds Ratios In Sas The Do Loop




Ppt Odds Vs Probability Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id




A Beginner S Guide To Interpreting Odds Ratios Confidence Intervals And P Values Students 4 Best Evidence



Are You Mixing Up Odds With Probability By Keith Mcnulty Towards Data Science




What And Why Of Log Odds What Are Log Odds And Why Are They By Piyush Agarwal Towards Data Science
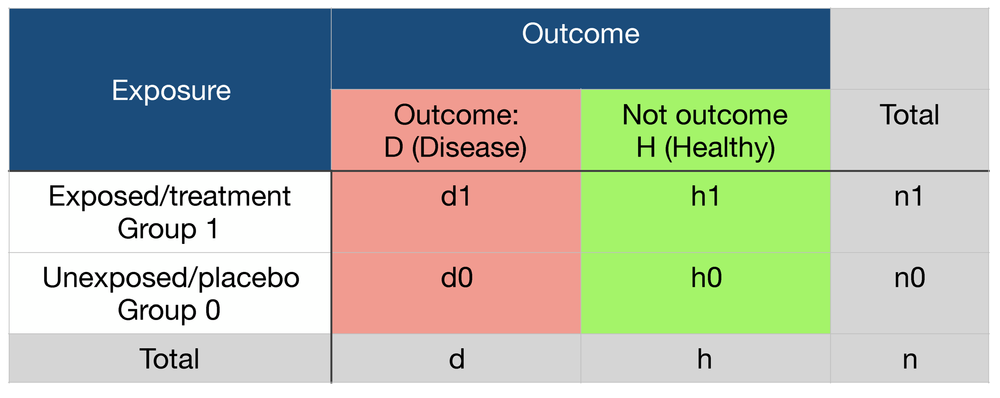



Probability Odds Ratio And Relative Risk Gp Raj




What Is The Difference Between Odds And Probability Statistics Youtube




How To Calculate Odds Ratio And Relative Risk In Excel Statology




Odds Vs Probabilities Odds Ratio In Spss Exp B Is An Odds Rather Than A Probability Odds Success Failure Probability Likelihood Of Success For Ppt Download



Proportions Chi Squared Tests And Odds Ratios
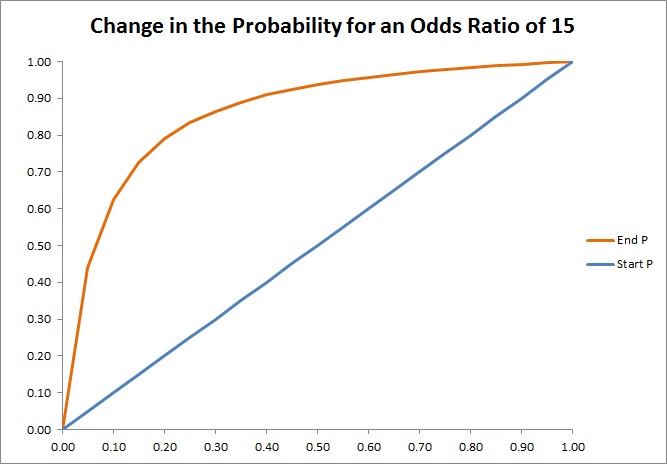



How To Convert Odds And Units To Probability Convert Odds To Percentage



What Are The Odds Stats With Cats Blog



Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1




Likelihood Ratio And Odds Ratio Slope Values Represent Odds As Shown Download Scientific Diagram



2 Odds Ghci Grade 12 Mathematics Of Data Management




Probability Vs Odds Youtube




Maximal Theoretical Effect Of Tests Odds Ratio Legend Or Log 10 Download Scientific Diagram



Graphpad Prism 9 Curve Fitting Guide Example Simple Logistic Regression




Estimated Z Score Odds Ratio And The Corresponding Probability For The Download Table



Odds Vs Risk Vantage Research




1 The Odds Ratio Relative Odds In A Case Control Study We Do Not Know The Incidence In The Exposed Population Or The Incidence In The Nonexposed Population Ppt Download



Against All Odds How To Visualise Odds Ratios To Non Expert Audiences Henry Lau




Solved 9 6 Odds To Probabilities 1 If The Odds Of An Chegg Com



Log Odds Definition And Worked Statistics Problems




Converting Between Probability And Odds Mathwoes Youtube



1




Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1
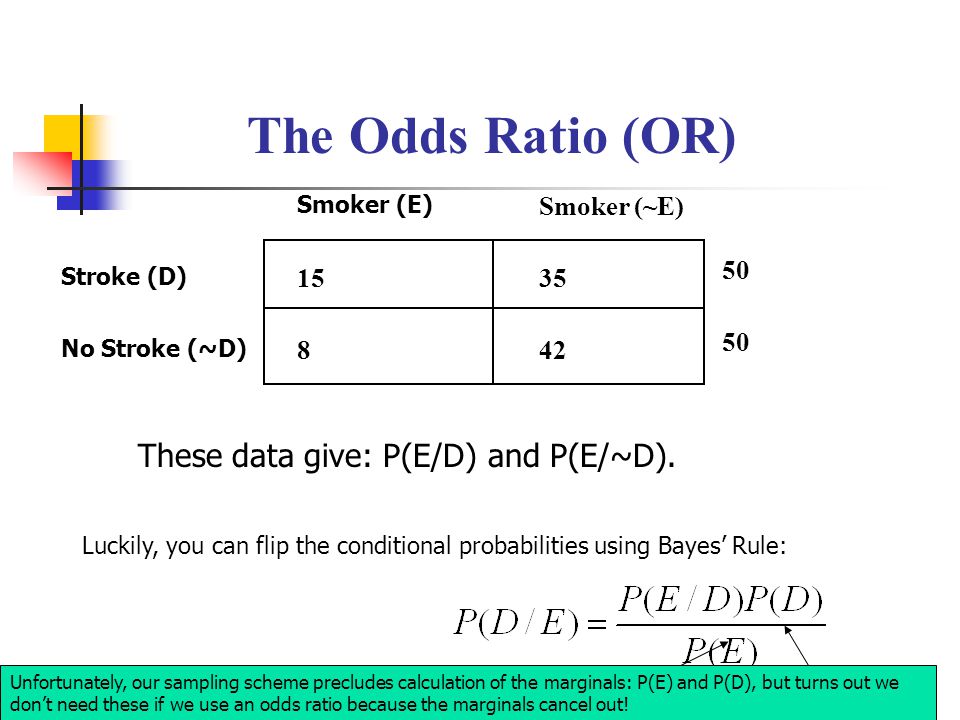



Conditional Probability Ppt Video Online Download




How To Calculate An Odds Ratio Youtube




Odds Ratios The Odd One Out Stats By Slough




Lecture3



Odds Likelihood Ratios Guide To Diagnostic Tests




How To Calculate Odds 11 Steps With Pictures Wikihow
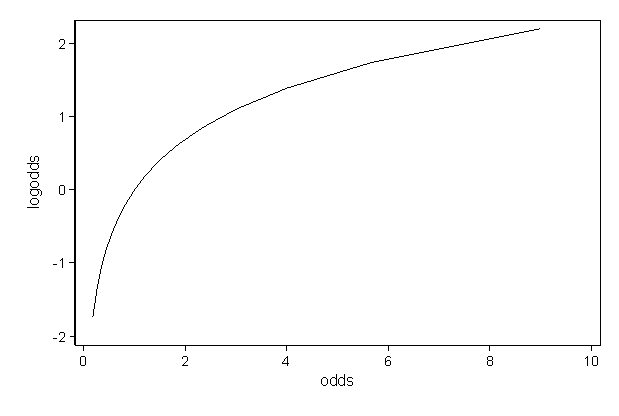



Faq How Do I Interpret Odds Ratios In Logistic Regression




Chapter 6 Choosing Effect Measures And Computing Estimates Of Effect Cochrane Training




Probability Vs Odds What S The Difference Learn It And By Z Ai Towards Data Science



Odds Ratio For A Simple Distribution Jmp User Community
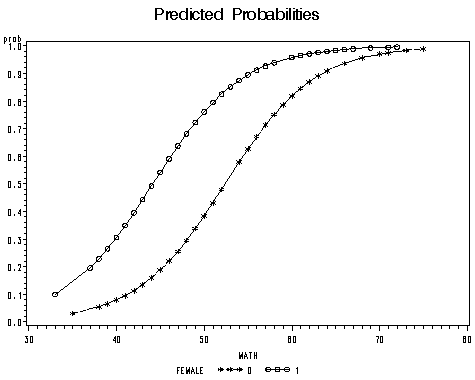



Proc Logistic And Logistic Regression Models




Facing Page Probability Of Survival And Odds Ratios For Death Download Scientific Diagram




Odds Ratio Relative Risk



Odds Vs Risk Vantage Research




Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1
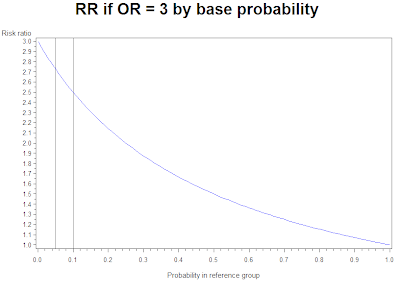



Example 8 29 Risk Ratios And Odds Ratios R Bloggers



1




Odds Ratio Wikipedia




Odds Ratio Relative Risk




Part 3 Module 3 Probability Suppose We Create



Odds Likelihood Ratios Guide To Diagnostic Tests




A Beginner S Guide To Interpreting Odds Ratios Confidence Intervals And P Values Students 4 Best Evidence




Lecture3
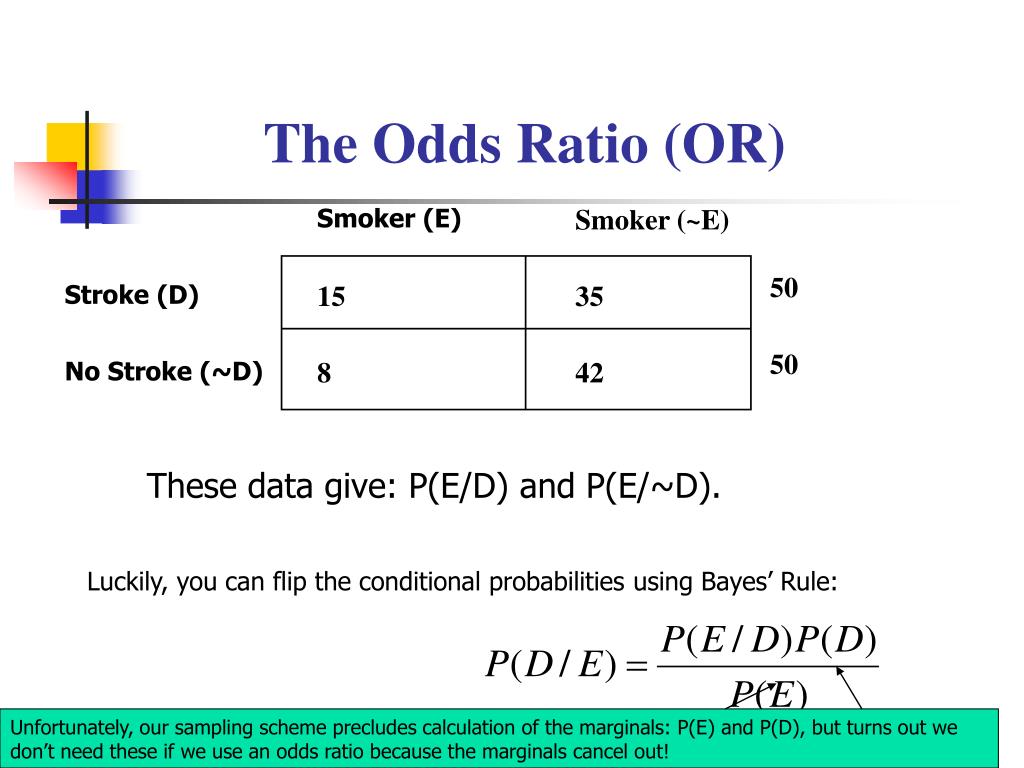



Ppt Conditional Probability Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id



Classification Methods And Assessment




Odds Ratio Relative Risk Calculation Definition Probability Odds Youtube




Probability And Odds Pptx Powerpoint




The Difference Between Relative Risk And Odds Ratios The Analysis Factor




Interpreting Odds Ratio Senguptas Research Academy




Odds Ratio Sage Research Methods



1




Statistics 12 Probability Vs Odds Stats Seandolinar Com




What Is An Odds Ratio And How Do I Interpret It Critical Appraisal



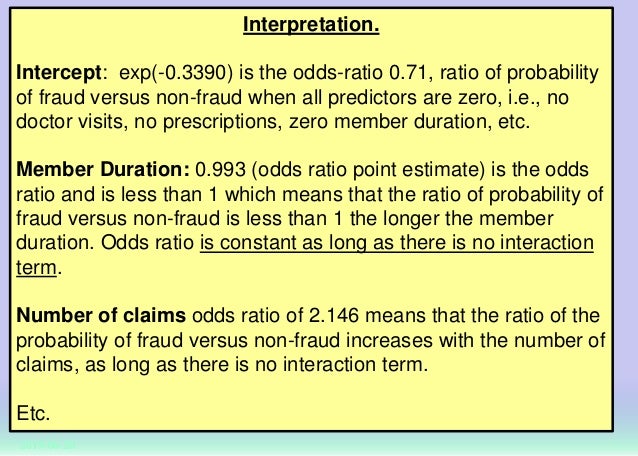
9 2 Binary Logistic Regression R For Health Data Science




Odds Ratio Calculation And Interpretation Statistics How To



Odds Ratios Basic Concepts
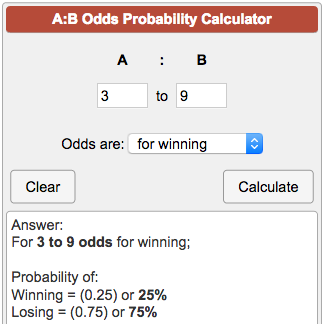



Odds Probability Calculator




Probability Vs Odds What S The Difference Learn It And By Z Ai Towards Data Science



Probability Vs Odds What S The Difference Learn It And By Z Ai Towards Data Science




Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios



The Difference Between Probability And Odds




R Calculate And Interpret Odds Ratio In Logistic Regression Stack Overflow




How To Calculate Odds 11 Steps With Pictures Wikihow




Talk Odds Ratio Wikipedia




Odds Ratio Wikipedia



Relative Risk Ratios And Odds Ratios




Binary Logistic Regression With Odds Ratios Calculated For The Download Table




Relative Risk Wikipedia




Logistic Regression In R Clearly Explained Youtube
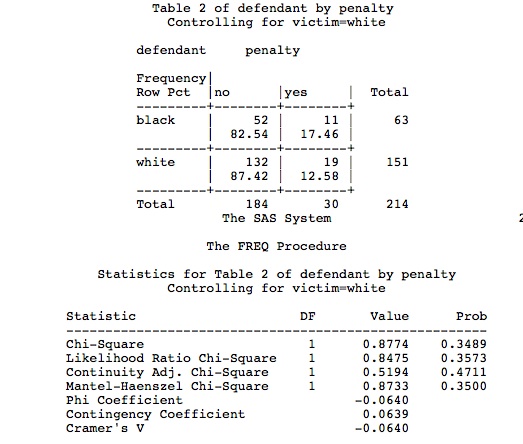



5 3 Marginal And Conditional Odds Ratios Stat 504




Relative Risks And Odds Ratios What S The Difference Mdedge Family Medicine




What Is An Odds Ratio And How Do I Interpret It Critical Appraisal
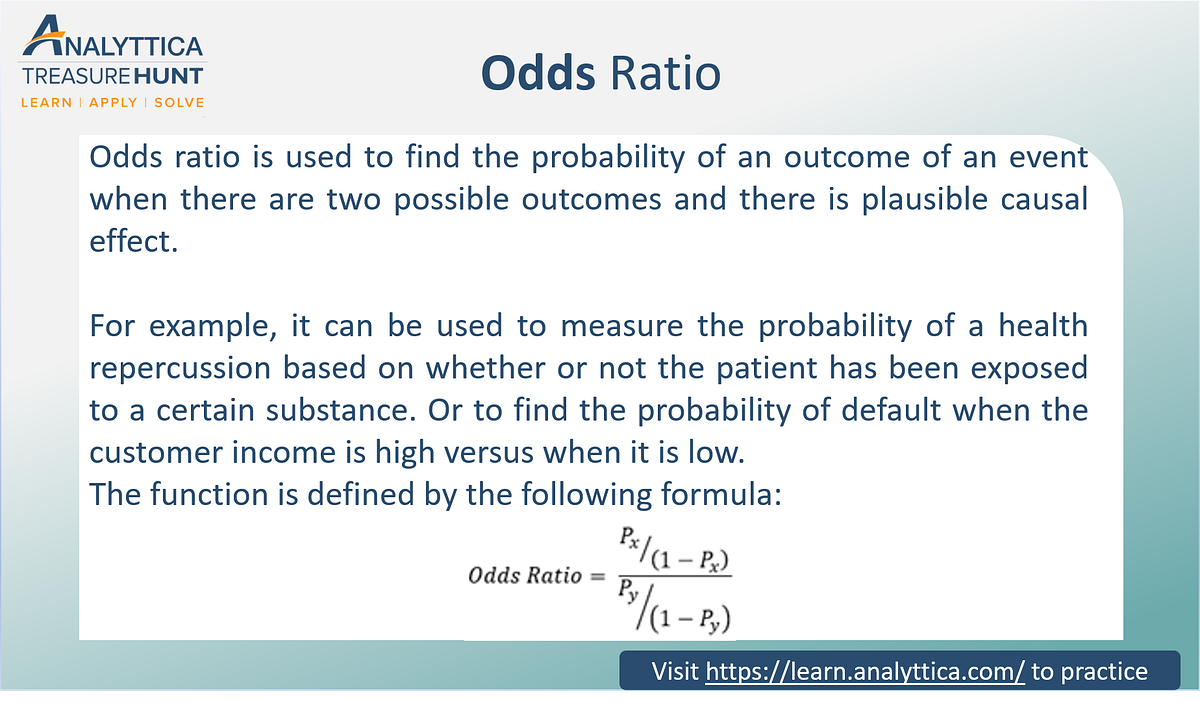



Odds Ratio The Odds Ratio Is Used To Find The By Analyttica Datalab Medium



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿